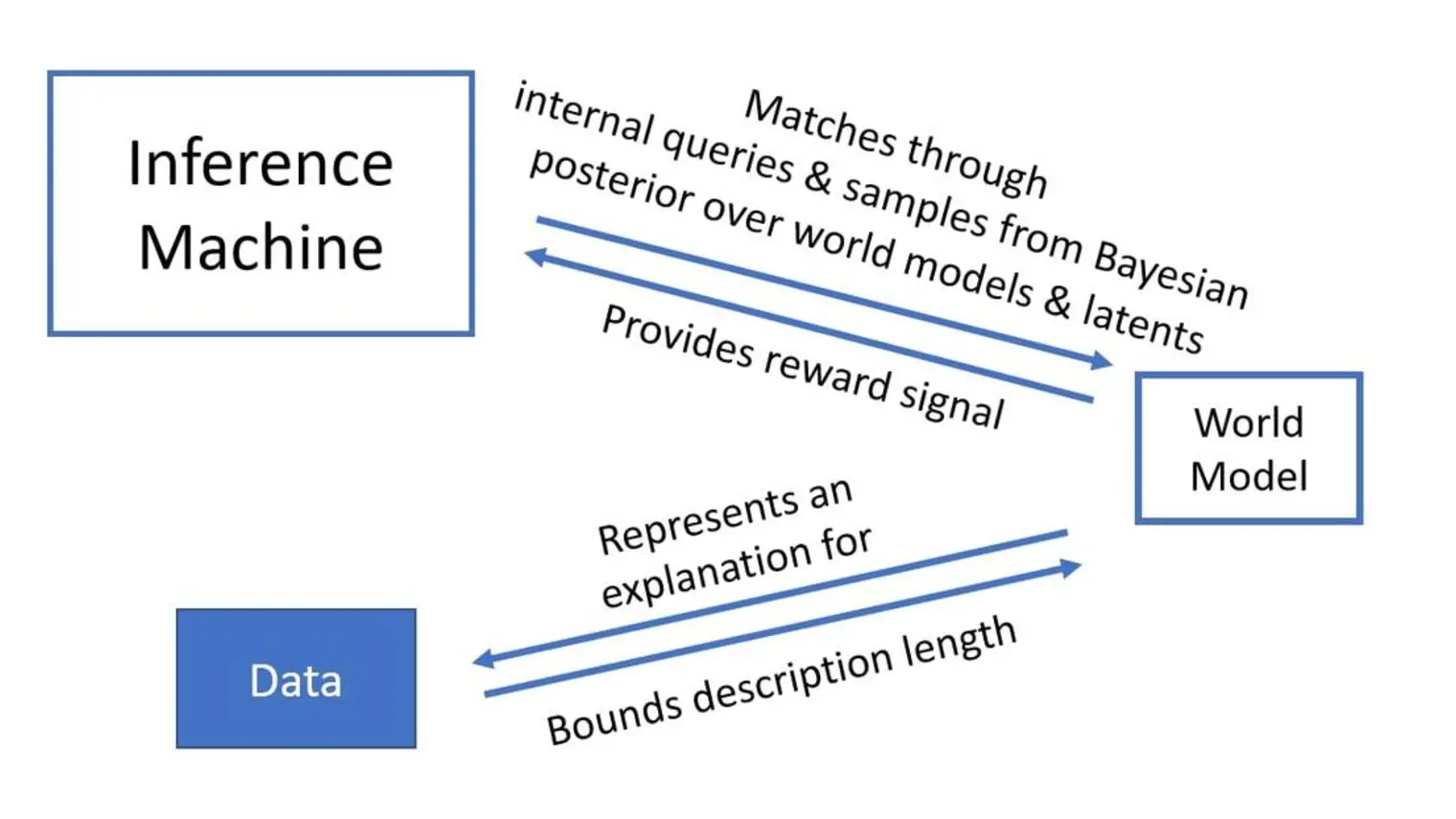
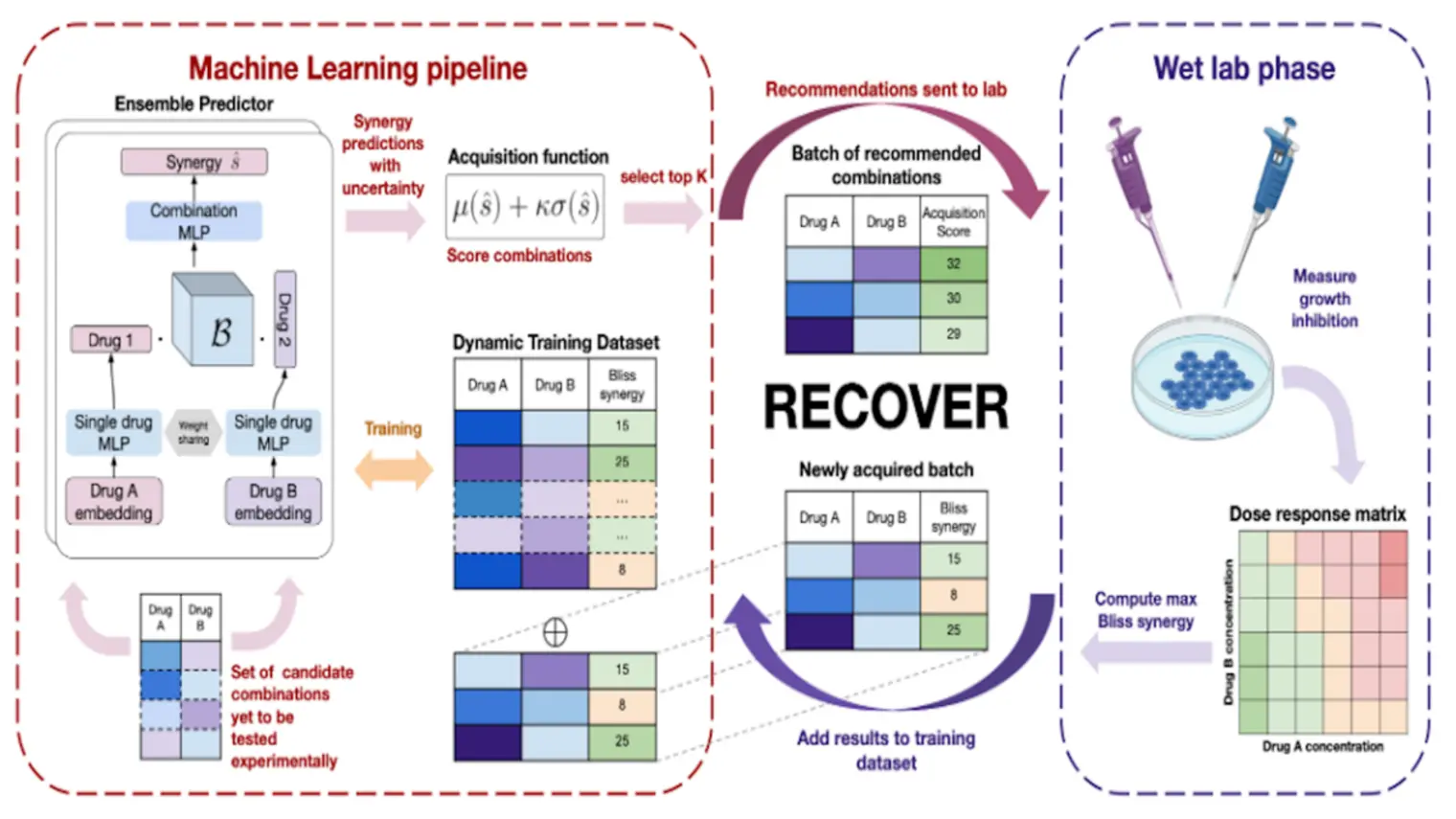
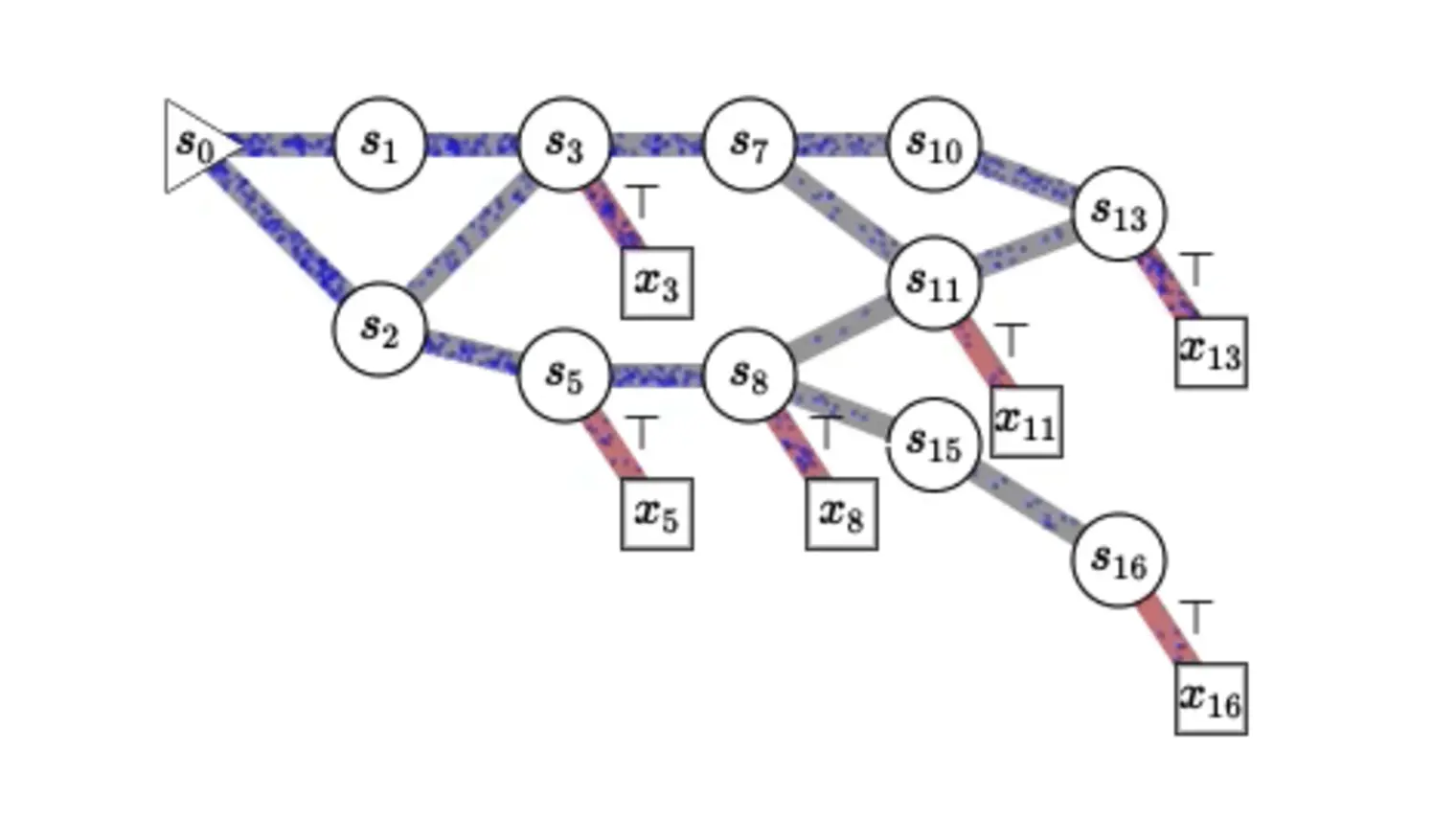
Yoshua Bengio
Biographie
*Pour toute demande média, veuillez écrire à medias@mila.quebec.
Pour plus d’information, contactez Cassidy MacNeil, adjointe principale et responsable des opérations cassidy.macneil@mila.quebec.
Reconnu comme une sommité mondiale en intelligence artificielle, Yoshua Bengio s’est surtout distingué par son rôle de pionnier en apprentissage profond, ce qui lui a valu le prix A. M. Turing 2018, le « prix Nobel de l’informatique », avec Geoffrey Hinton et Yann LeCun. Il est professeur titulaire à l’Université de Montréal, fondateur et conseiller scientifique de Mila – Institut québécois d’intelligence artificielle, et codirige en tant que senior fellow le programme Apprentissage automatique, apprentissage biologique de l'Institut canadien de recherches avancées (CIFAR). Il occupe également la fonction de conseiller spécial et directeur scientifique fondateur d’IVADO.
En 2018, il a été l’informaticien qui a recueilli le plus grand nombre de nouvelles citations au monde. En 2019, il s’est vu décerner le prestigieux prix Killam. Depuis 2022, il détient le plus grand facteur d’impact (h-index) en informatique à l’échelle mondiale. Il est fellow de la Royal Society de Londres et de la Société royale du Canada, et officier de l’Ordre du Canada.
Soucieux des répercussions sociales de l’IA et de l’objectif que l’IA bénéficie à tous, il a contribué activement à la Déclaration de Montréal pour un développement responsable de l’intelligence artificielle.