Yoshua Bengio
Biography
*For media requests, please write to medias@mila.quebec.
For more information please contact Cassidy MacNeil, Senior Assistant and Operation Lead at cassidy.macneil@mila.quebec.
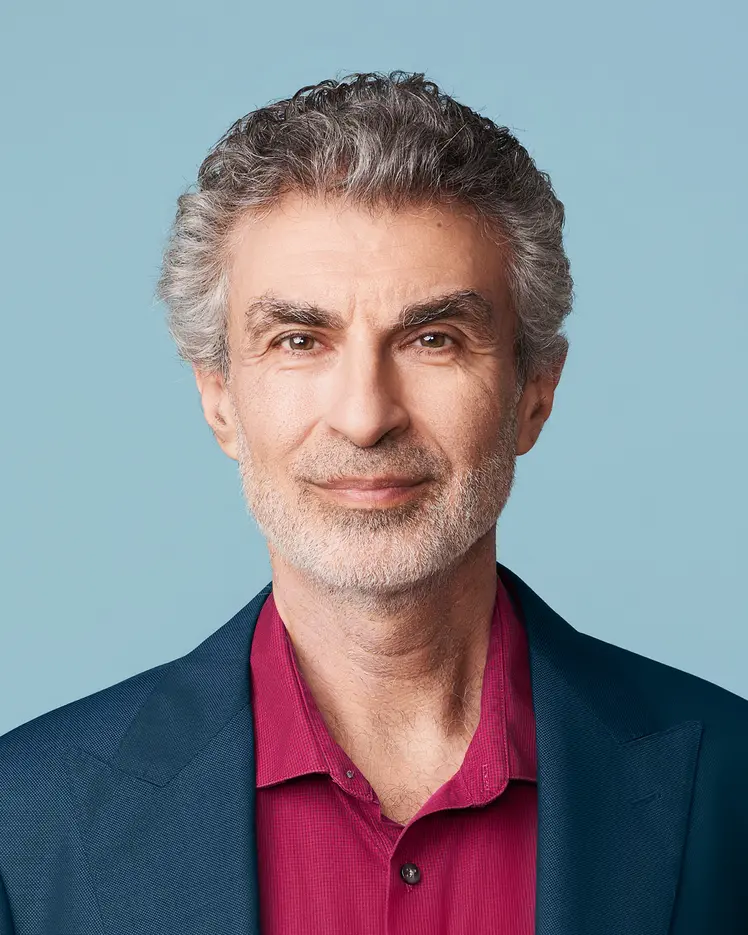
Yoshua Bengio is recognized worldwide as a leading expert in AI. He is most known for his pioneering work in deep learning, which earned him the 2018 A.M. Turing Award, “the Nobel Prize of computing,” with Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun.
Bengio is a full professor at Université de Montréal, and the founder and scientific advisor of Mila – Quebec Artificial Intelligence Institute. He is also a senior fellow at CIFAR and co-directs its Learning in Machines & Brains program, serves as special advisor and founding scientific director of IVADO, and holds a Canada CIFAR AI Chair.
In 2019, Bengio was awarded the prestigious Killam Prize and in 2022, he was the most cited computer scientist in the world by h-index. He is a Fellow of the Royal Society of London, Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada, Knight of the Legion of Honor of France and Officer of the Order of Canada. In 2023, he was appointed to the UN’s Scientific Advisory Board for Independent Advice on Breakthroughs in Science and Technology.
Concerned about the social impact of AI, Bengio helped draft the Montréal Declaration for the Responsible Development of Artificial Intelligence and continues to raise awareness about the importance of mitigating the potentially catastrophic risks associated with future AI systems.