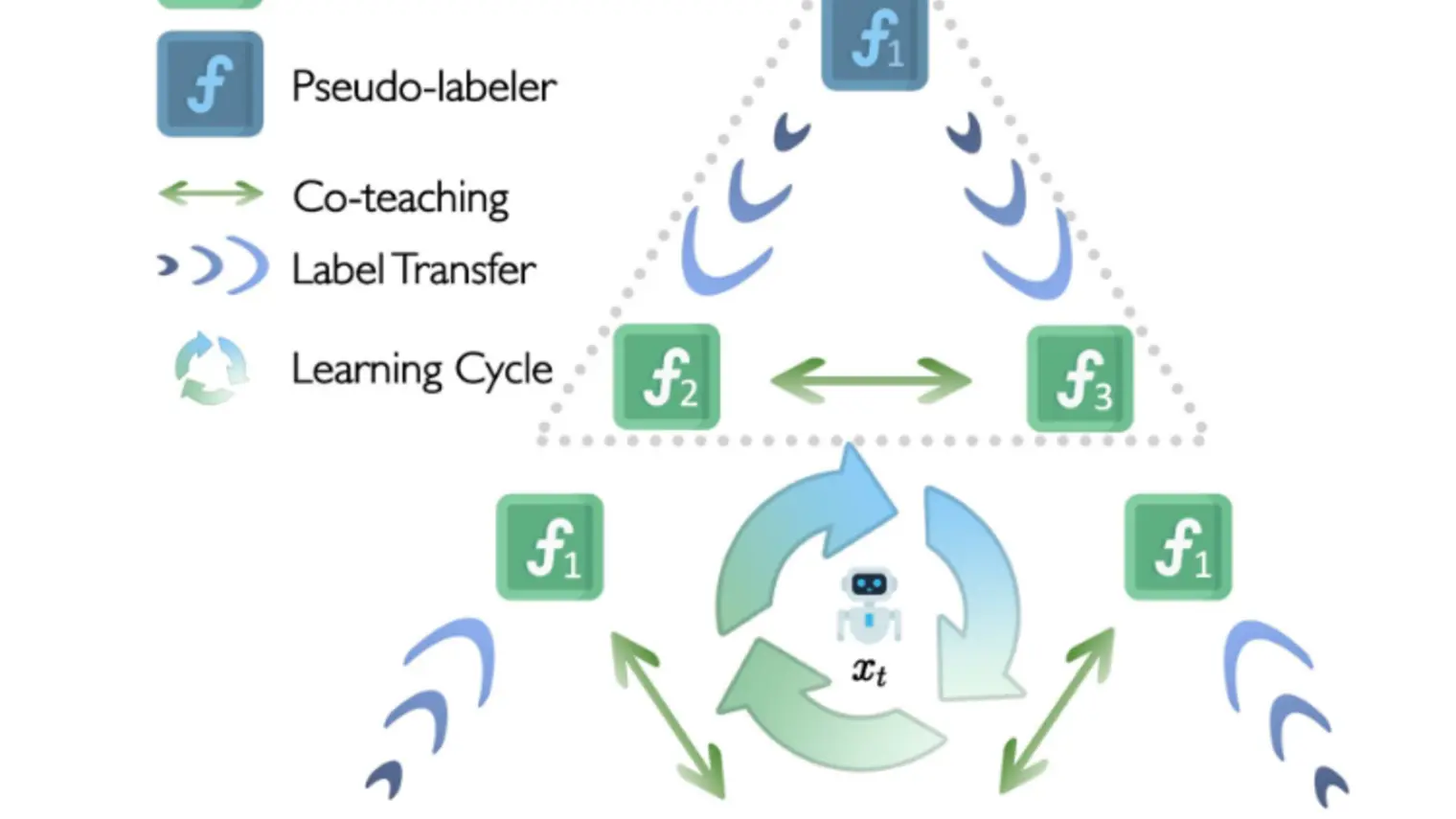
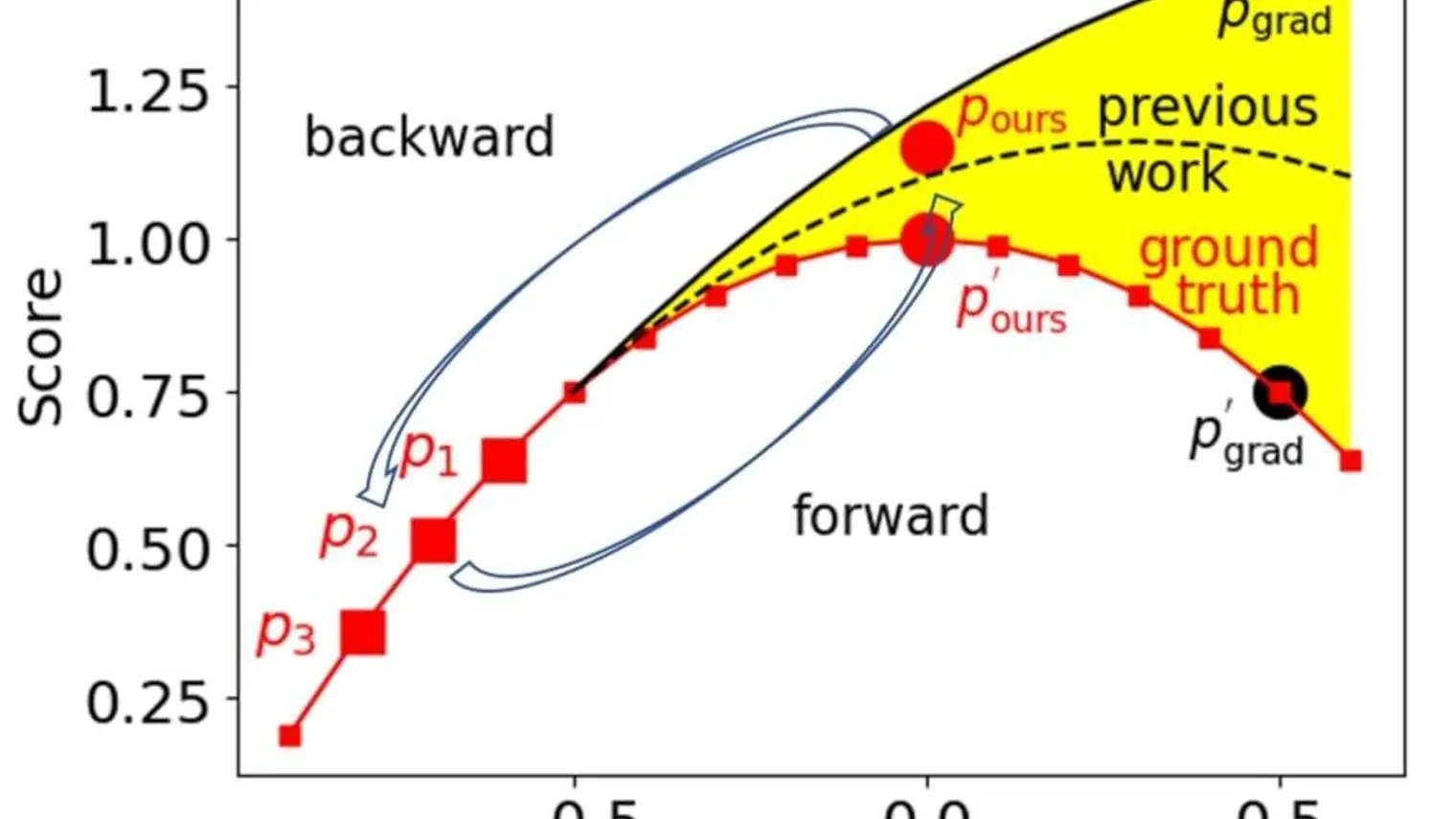
Xue (Steve) Liu
Biographie
Xue (Steve) Liu est professeur titulaire à l'École d'informatique de l’Université McGill, ainsi que vice-président de la recherche et du développement, scientifique en chef et codirecteur du Centre d'IA de Samsung à Montréal. Il est également titulaire d'une bourse William Dawson (professeur titulaire) à l'Université McGill et professeur de mathématiques et de statistiques (nomination de courtoisie) dans le même établissement. Auparavant, il était scientifique en chef chez Tinder Inc., où il dirigeait la recherche et l'innovation touchant l’application de rencontre et de découverte sociale la plus importante au monde, évaluée à plus de 10 milliards de dollars américains.
M. Liu est membre de l'IEEE et membre associé de Mila – Institut québécois d’intelligence artificielle. À l'Université McGill, il est également membre associé du Centre sur les machines intelligentes (CIM) et du Centre sur les systèmes et les technologies avancés en communication (SYTACom). Il a reçu plusieurs récompenses, notamment le prix Mitacs 2017 reconnaissant un leadership exceptionnel parmi le corps professoral, le prix Outstanding Young Canadian Computer Science Researcher de l'Association canadienne de l'informatique en 2014, et le prix Tomlinson Scientist soulignant l'excellence et le leadership scientifique à l'Université McGill. Il est le directeur du Laboratoire sur l’intelligence cyberphysique de l'Université McGill, qu’il a fondé en 2007. Il a également travaillé brièvement en tant que professeur associé de la chaire Samuel R. Thompson au Département d'informatique et d'ingénierie de l'Université du Nebraska à Lincoln, aux laboratoires Hewlett-Packard à Palo Alto, en Californie, et au centre de recherche T. J. Watson d'IBM à New York.